Cloud technology has become a game changer for financial services, helping them meet evolving customer expectations and adapt to a dynamic landscape. Multi-cloud for financial services enhances these capabilities, offering a competitive advantage over traditional infrastructure, which is prone to failure.
While many financial services firms initially adopted hybrid cloud models to balance flexibility with regulatory requirements, a growing number are now turning to multi-cloud strategies. This shift reflects the increasing demand for agility, scalability, and resilience. By leveraging multiple public cloud providers alongside private infrastructure, firms can avoid vendor lock-in, enhance performance, and better manage risk. Whether it’s a FinTech startup with no legacy systems or a traditional institution undergoing digital transformation, the ability to rapidly innovate and adapt is driving the move toward multi-cloud data management.
What is Multi-cloud Data Management?
A multi-cloud approach is a strategy where organizations utilize multiple cloud computing platforms to perform various tasks. This approach helps avoid dependency on a single vendor, allowing organizations to select resources from different providers and leverage the unique benefits of each service.
A multi-cloud solution might include the distribution of cloud assets, data, software, and applications. It combines software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) across both private and public cloud environments.
Key Drivers of Multi-cloud Adoption in Financial Services
A multi-cloud architecture helps reduce financial risks while adhering to established data governance and security controls. Additionally, the following factors accelerate the drive for multi-cloud strategies:
- Better return on investment: Multi-cloud enables stakeholders to select specific solutions that best meet their organization’s needs, ensuring optimal resource utilization and cost efficiency.
- Freedom of choice: A single cloud provider may not be able to cater to all the computing services an organization requires. Having a choice of service providers allows flexibility.
- Containerization: Containers isolate applications and related libraries, ensuring efficient resource utilization, even in pooled environments.
- Reduced time to market: Technologies like software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NVF) simplify configuration management, enhancing agility and speeding up time-to-market for new services.
- High reliability: Multi-cloud solutions reduce the risk of a single point of failure as they create redundancies to depend on. This ensures a more resilient architecture.
- Better disaster recovery: The likelihood of simultaneous outages or downtimes across multiple cloud vendors is minimal. This improves business continuity and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Provider-specific services: Organizations can choose services and infrastructure from different cloud providers that align closely with their unique business needs.
- Enhanced scalability: Multi-cloud environments allow enterprises to quickly scale resources seamlessly across providers as demand increases.
- Reduced latency: Dispersed organizations can reduce latency by choosing local public cloud vendors, based on each facility’s geographic location.
- Reduced footprint and lower costs: A multi-cloud strategy helps avoid the need to build and maintain physical data centers, with virtual data centers significantly reducing infrastructure costs.
- AI and machine learning enablement: Multi-cloud environments are becoming important for deploying artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications in financial institutions. These technologies are used for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, personalized customer service, and risk management. A multi-cloud approach allows firms to choose AI/ML services from different providers, optimizing performance and cost for specific workloads.
- Serverless computing: The use of serverless computing in multi-cloud architectures is increasing within financial services. Serverless technologies enable firms to run code without managing servers, reducing operational overhead and improving scalability for event-driven applications such as real-time fraud detection and automated customer onboarding.
Challenges of Multi-cloud Adoption in Financial Institutions
- Growing cloud costs: Signing up for and deploying an increasing number of cloud apps/service providers can result in an uptick in spending. Organizations should adopt strong FinOps practices by using cloud cost management tools to track spending, optimize costs, and automate resource provisioning. Regularly reviewing cloud usage helps eliminate underutilized resources and minimize waste.
- Rapid changes in arrangements: As an increasing number of cloud apps are added to IT environments, organizations risk losing control of identity processes, access management, and security. To address these challenges, a centralized identity and access management (IAM) system that integrates with all cloud providers is necessary. In addition, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enforcing the principle of least privilege access across all cloud environments are essential measures.
- Specialist management expertise: Effective multi-cloud management requires specific expertise to ensure that an organization’s IT environment remains available and secure at all times, while minimizing the risks of increased costs and complexity. The shortage of skilled cloud professionals presents a considerable challenge to multi-cloud adoption. To address this skills gap, organizations should invest in training programs, certifications, and partnerships with cloud service Additionally, adopting automation tools and partnering with managed services providers can alleviate the burden on internal IT teams.
- Security concerns: Businesses need to assess their legacy networks, environments, and security architectures before implementing multi-cloud to avoid potential risks and liabilities. Financial institutions encounter increasingly complex cyber threats, including ransomware, supply chain vulnerabilities, and insider attacks. A multi-cloud setup can add new risks if not secured properly. Essential security measures include multi-factor authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. Cloud-native security solutions offering centralized visibility and control are also recommended.
- Data privacy and protection: Maintaining data privacy, controlling data access, and preventing data breaches when data is distributed across various cloud providers and regions, each with potentially different security and compliance standards, can be challenging. Organizations must ensure seamless access to all cloud services, maintain least privilege access across cloud environments, and establish a robust identity architecture that federates with any application or service. Encrypting data at rest and in transit, establishing clear data governance policies and procedures to ensure compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and regularly auditing data access and usage to identify and address potential privacy risks are a must.
Also read: Data Management Trends and Best Practices for Financial Services
Current state of financial services infrastructure hampering operational efficiency
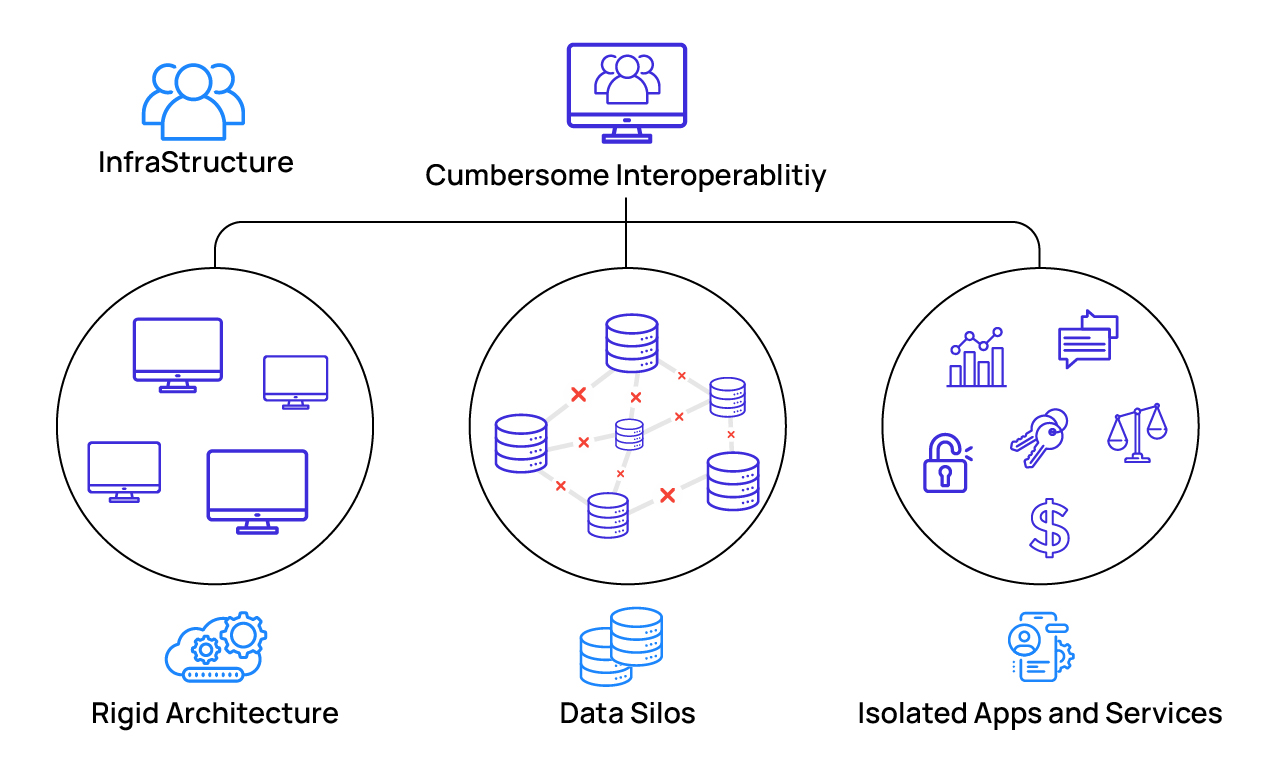
Optimized infrastructure for modern financial services data management
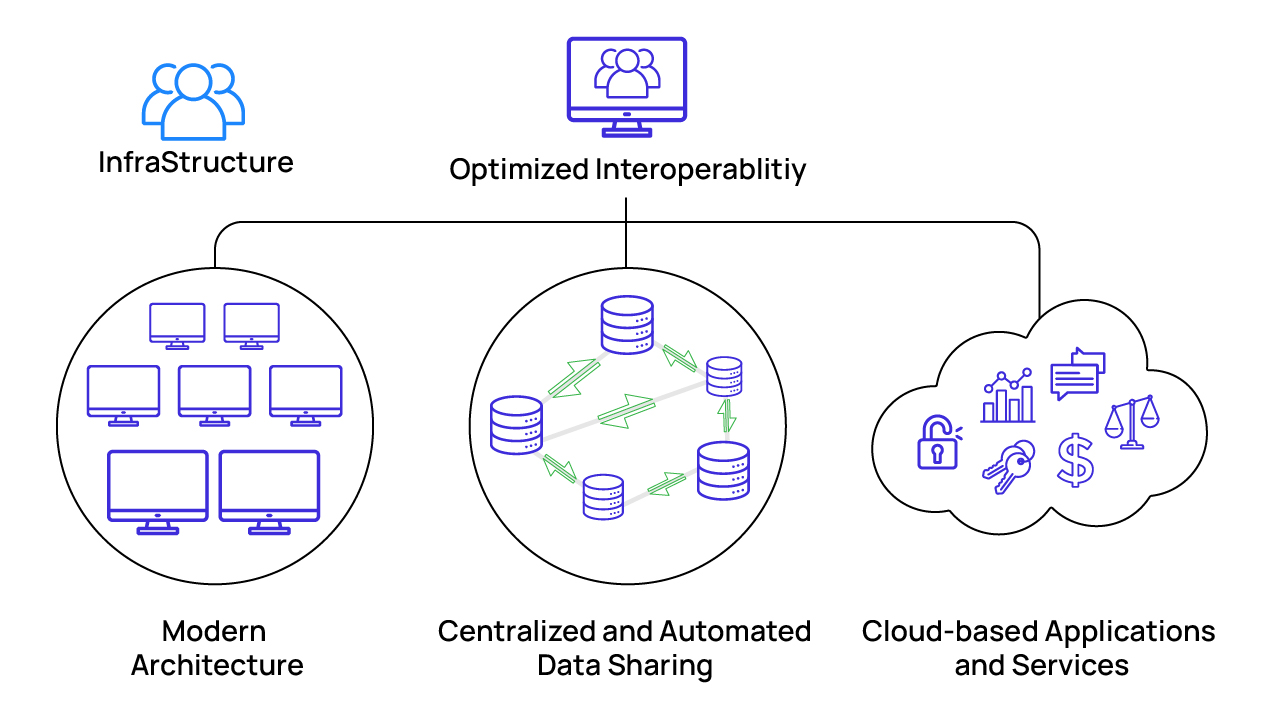
Multi-cloud for Financial Services Data Management
Modern data management solutions must seamlessly integrate with multi-cloud environments to enhance the agility, flexibility, and efficiency of financial services providers while meeting security and compliance needs. These solutions should ensure real-time, uninterrupted access to cloud resources and support all major cloud platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Snowflake, etc., enabling organizations to leverage the strength of multiple vendors.
Key architectural considerations for effective multi-cloud data management include:
Extensible APIs and interoperability: The solution should feature extensible APIs and robust interoperability to facilitate seamless integration across diverse cloud platforms.
Cybersecurity and compliance: Strong cybersecurity measures and comprehensive compliance management are critical to safeguarding sensitive financial data and meeting regulatory standards.
Flexible storage: Flexible storage capabilities allow organizations to segregate and manage different databases across multiple platforms based on specific requirements like cost savings and operational efficiency. For example, reference data like security master or price master could be hosted on one cloud, while investment data could reside on another platform, all while maintaining integration for seamless access and analysis.
Cloud for Financial Services: Overcoming Challenges with Hexaware
Hexaware’s low-code, no-code enterprise data management solutions for financial services address the challenges of legacy solutions while empowering customers with actionable insights for enhanced visibility and accelerated business innovation.
Key features include:
- API orchestration for multi-cloud strategy: Built-in API orchestration enables users to seamlessly switch between cloud platforms for data consumption or dashboard visualization based on their specific needs.
- Comprehensive business glossary: A rich glossary with business definitions for each capital market domain and robust data lineage capabilities ensures streamlined data governance and compliance management.
- Multi-cloud integration: Flexibility to integrate with leading cloud vendors for enhanced business agility and operational efficiency.
Ready to modernize your data management processes and achieve greater adaptability with multi-cloud data management? Contact us at marketing@hexaware.com to learn how we can help you.



















