This website uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies
Driving Cloud Value: Optimizing Cloud Cost with Hexaware’s Cloud Financial Management Framework
Cloud
May 18, 2023
Cloud financial management is the process of managing and optimizing the financial aspects of cloud computing resources, including the cost, usage, and performance of cloud services. It involves implementing strategies, chargeback or showback processes, budgeting, forecasting, and tools to monitor, control, and optimize cloud expenditure. It also comprises leveraging data analytics and machine learning to gain insights into cloud usage patterns and identify cost savings and optimization opportunities.
Organizations that effectively manage their cloud financials can make informed decisions about their cloud usage, allocate resources more effectively, and gain insights into their cloud spend.
Some commonly used tools for cloud financial management include cloud cost management platforms, cost allocation tools, and billing and invoicing systems. These tools can help organizations track their cloud spend, optimize resource usage, and gain insights into cloud usage patterns.
Optimizing cloud costs can become intimidating for enterprises as it requires careful planning and a deep understanding of the technology and services involved in the cloud computing environment. The challenges of cloud financial management involve various areas, including budgeting, forecasting, tracking, and compliance.
As a strategic cloud consulting partner, Hexaware can assist enterprises in setting up cost management practices, implementing the right security controls, and driving financial accountability while accelerating innovation and business value.
Hexaware’s Cloud Financial Management Framework
Let’s look at the 4 phases of Hexaware’s cloud financial management framework to understand how they help an organization achieve its goal of optimizing its cloud footprint.
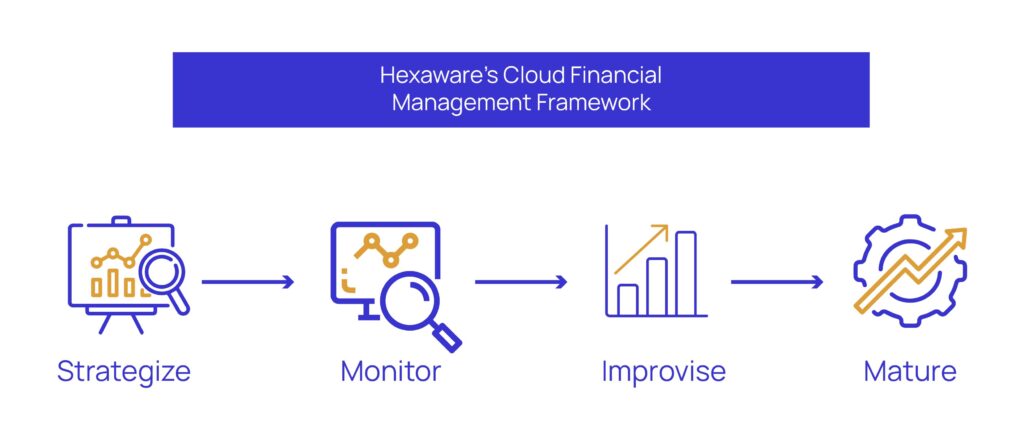
1. Strategize
The foundation for a successful cloud journey is laid during this phase, and it is one of the most strategic and important steps in cloud financial management. The critical factors to be considered for accurate planning are:
Requirement gathering
Articulate technology and architecture requirements based on business requirements, performance, compliance, and security of the current setup while considering the future roadmap.
Cost-conscious architectural design
Develop the most cost-effective strategy by monitoring resource utilization and maintaining high availability, scalability, and data integrity while keeping security in mind.
Explore available pricing models
Identify the available pricing models, for example, Pay-As-You-Go, enterprise agreement, commitment-based spending, based on tenancy model (single tenant infrastructure vs. multi-tenant infrastructure), embedded license-based software, etc.
Forecast workload
Forecasts based on assumptions contain a margin of error. Application teams should analyze their current hardware and software configurations and review and predict their workload using AI/ML-based algorithms or third-party tools for efficient and accurate forecasts.
Define budget threshold
Establishing budget thresholds for the underlying workloads running on the cloud is important to give a sense of ownership and accountability. This also helps the team better plan and monitor their spending to keep it on track.
2. Monitor
Once the requirement gathering and budget planning are done, the next step is implementing, tracking, and monitoring the resource and cost spending to get the right insights:
Define resource hierarchy
Define a strategy for resource hierarchy structure to segregate workload based on department, environment, or application group for resource isolation and management at scale.
Resource tagging
Develop tagging strategies and guidelines to identify, manage, and organize resources. This empowers the application team to search and filter the desired cloud resources. Organizations can use tags like vertical, department, application, environment, application owner, and others per the business needs. Here are a few advantages of implementing a resource tagging strategy:
- Implement showback and chargeback process
- Break down cost report
- Identify orphan resources and associated cost
- Identify unused resources and associated cost
- Cloud spend vs. On-prem (for specific workload)
Apportion charges for shared resources
Define strategy and model for charging back application teams or splitting the charges for shared resources.
Automated anomaly detection
Monitoring cloud expenditures can be arduous and time-consuming. Using a policy, define the conditions that may constitute an anomaly. Automate the detection and notification of deviations from normal trends. Predict the potential evolution of the normal value range over time.
3. Improvise
Real cost optimization is thinking beyond cost reduction and exploring how you should be doing certain things to understand and realize the cost benefits:
Rightsize cloud resources
Collect and monitor resource utilization and cost-related details. Assess the reports and suggestions shared by respective CSPs for rightsizing. Provide rightsizing recommendations to application teams and prioritize and monitor them until implemented.
Reserved vs. preemptible instances
- Use reserved instances for a well-defined and consistent workload.
- Use preemptible instances for workloads (e.g., batch jobs) that are not affected due to unavailability or infrastructure capacity issues. Workloads can resume once the infrastructure issue is resolved or the capacity is released. For e.g., Azure Spot and AWS EC2 Instances.
Enable auto-scaling
Evangelize the concept of automatic scaling to create and delete resources automatically based on the varying workloads and well-defined threshold boundaries.
Power scheduling
Lay out instructions and enforce application teams to schedule a shutdown for cloud resources and pause computing as much as possible. Discuss with the app team and help them automate the shutdown of Prod and Non-Prod VMs post-business hours on weekdays and weekends.
Delete unused & orphan resources
Lay out a plan to identify idle orphan resources. Run reports periodically to identify such resources and notify application teams to act accordingly. Integrate cloud resource lifecycle (including decommissioning) with enterprise CMDB and ITSM tools.
Manage and minimize cost anomalies
Use the Cost Anomaly Detection services CSPs offer to detect, alert, and promptly manage unexpected or unforecasted cloud cost events.
Implement organizational strategies
The CCoE should provide guidance, develop, and implement strategies to achieve the following long-term organizational goals:
- Determine and publish the categorical list of services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) for use (if operating in a multi-cloud environment) only from a certain CSP. For e.g., VMs from Azure.
- Provide end users with real-time comparative costs for popular services (in tabular format) for different regions for each CSP. For e.g., VMs.
- Automate deletion of resources created for training purposes from the sandbox environment periodically to keep a check on cost.
- Automate mundane administrative work. For e.g., enforcing tags, tracking resources, and associated costs.
- Build dashboards and reports, and create policies to track, govern, and optimize cloud spend.
4. Mature
The final phase after cost optimization is to further optimize the cost strategy from the learnings and improve the cost benefits by considering the following:
Develop a tooling strategy
Managing cloud costs go beyond spreadsheet management. Organizations should deploy real-time tools that read metrics using APIs and automate the process to enable scalability. Use cloud-native services along with third-party tools and develop your API extensions to visualize utilization and efficiently manage and optimize cloud costs.
Evaluate new providers
Evaluate and onboard new cloud providers based on the following pointers:
- CSP offerings, cloud-native services, pricing models, SLAs, etc.
- Establish vendor-specific KPIs.
- Review the cloud provider’s terms and conditions.
Evaluate alternate cloud providers
Develop cost-based workload placement policies that govern the decision of the target cloud provider for the applications. Consider different technology platforms, available services, design principles, HA strategies, security, and SLAs offered to compare the costs of other cloud providers. This helps teams build applications for the future, considering cost savings from cloud-induced efficiencies.
Budget accountability
Shift budget accountability to application teams to manage cloud usage efficiently. Implement centralized initiatives to reduce costs and remove waste, formalize budget approval to enable users to access cloud-based services, and give consumers real-time spending visibility.
Encourage financial management practices
Gamify cost management practices and incentivize the winning teams. Create dashboards ranking teams based on their savings, spending discipline, unaddressed spending waste, cost optimization opportunities, etc., and include an increase/decrease indication in metrics from the previous month’s value.
Establish business value with cloud investment
Educate application teams to consider cloud cost as an investment and encourage them to correlate cloud costs to business KPIs and calculate the ROI.
Cloud financial management is integral to managing a business in the modern era. Effective cloud financial management helps organizations maximize the value of their cloud investments, minimize costs, and improve overall performance. With the right tools and processes, Hexaware can help organizations set up cloud economics using its guidance framework.
This framework assists organizations in carefully analyzing the potential challenges of cloud financial management and strategically planning their cloud investments to realize the full potential of the cloud. It can be executed on all major cloud service providers – AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, allowing enterprises to work on the phases independently according to their business needs.
About the Author

Pawan Modi
Read more
Related Blogs

Understanding Snowflake Cortex for Gen AI Applications with Sensitive Data
- Data & Analytics
- Generative AI
- Cloud

Ready to Pursue Opportunity?
Every outcome starts with a conversation