This website uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies
Ensuring Robust Cloud Security: Safeguarding Data in the Digital Age
Cloud
August 1, 2023
Despite the promise and flexibility that the cloud offers, security is something that companies cannot compromise on!
In today’s digital landscape, protecting organization data and applications from cyber threats is an essential and constant responsibility for enterprises of all sizes. As more organizations transition to the cloud, establishing a reliable cloud security posture has become crucial and is part of board discussions.
The cloud offers numerous advantages, such as scalability, cost-efficiency, and agility. However, with these benefits come concerns about security. As organizations migrate workloads and sensitive information to the cloud, it becomes imperative to implement robust security measures to safeguard data and applications from potential threats.
In this blog post, we will explore the importance of cloud security and discuss key strategies to ensure the protection of valuable assets in the cloud.
Understanding Cloud Security
Growing adoption of cloud computing has brought forward a lot of security concerns for organizations. One of the biggest mistakes companies can make is implementing a cloud solution without much consideration of its cloud security. Cloud security refers to the set of practices, technologies, and policies implemented to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud environments. It involves addressing various security challenges, including data breaches, unauthorized access, data loss, and service disruptions, resulting in financial losses and damage to the reputation. Cloud security aims to provide confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data stored in the cloud while ensuring compliance with regulations and industry standards.
Key Challenges and Security Risks in the Cloud
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data remains a top concern for organizations. Breaches can occur due to weak authentication, insecure APIs, or vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure.
- Data Loss: Data loss can result from accidental deletion, system failures, or natural disasters. Effective backup and disaster recovery strategies are crucial to mitigate the impact of data loss incidents.
- Insider Threats: Internal actors, such as employees or contractors, can pose security risks by intentionally or accidentally compromising data. Insider threats necessitate strong access controls, behavior analysis, and monitoring mechanisms.
- Lack of Control and Visibility: When data and applications are moved to the cloud, organizations often lose a certain level of control and visibility over their infrastructure. This can make it challenging to monitor and manage security effectively.
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Organizations must adhere to industry-specific regulations and data protection laws when handling sensitive data in the cloud. Compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS require robust security measures to protect customer information.
- Insecure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs): Any API built into your web or mobile applications can offer access internally by staff or externally by consumers. It is external-facing APIs that can introduce a cloud security risk. Any insecure external API is a gateway offering unauthorized access by cybercriminals looking to steal data and manipulate services.
- Zero-day Attacks: These are the attacks that are targeted by hackers on recently identified vulnerabilities in the software and applications on the cloud. System administrators get a little window of time to fix these vulnerabilities by applying patches.
Strategies for Robust Cloud Security
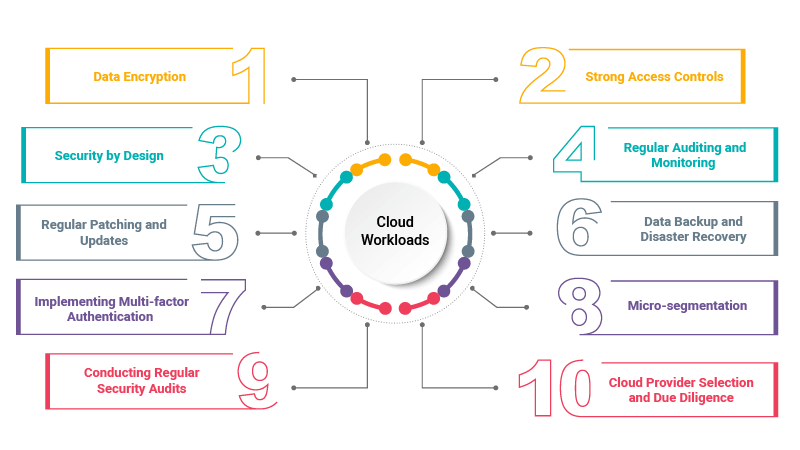
- Data Encryption: Encryption plays a critical role in securing data stored in the cloud. It involves converting information into an unreadable format, which can only be accessed with the correct decryption key. Employing strong encryption algorithms ensures that even if data is compromised, it remains unusable to unauthorized individuals. Similarly, encrypting data in transit protects it from interception and unauthorized viewing. Implement robust encryption mechanisms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), and securely manage encryption keys to safeguard sensitive information.
- Strong Access Controls: Implementing strict access controls is vital to prevent unauthorized access to cloud resources. Multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, and role-based access controls (RBAC) should be enforced to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. Implement the principle of least privileges, granting users only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks.
- Security by Design: It is essential that security should be included in the design phase of the cloud adoption process. For example, you can make use of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to spin up cloud infrastructure like compute, databases, applications, networks, etc., with appropriate security controls baked in from the start.
- Regular Auditing and Monitoring: Continuous monitoring and auditing of cloud infrastructure and applications help detect and respond to security incidents promptly. Robust logging mechanisms, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions should be implemented to identify potential threats and unusual activities.
- Regular Patching and Updates: Cloud service providers regularly release patches and updates to address security vulnerabilities. Timely implementation of these updates helps protect against known exploits and strengthens the overall security posture of cloud environments.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Regular backups and a comprehensive disaster recovery plan are essential to mitigate the risk of data loss and ensure business continuity. Backups should be stored in secure off-site locations or replicated across multiple cloud regions for redundancy.
- Implementing Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Multi-factor Authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification to access cloud resources. MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Enforcing MFA across all user accounts, including administrators, is a critical security measure.
- Micro-segmentation: It is the practice of dividing your cloud deployment into separate security segments, right down to the individual workload level. By isolating individual workloads, you can apply flexible security policies to minimize any damage an attacker could cause should they gain access.
- Conducting Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits and assessments are vital for identifying vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance, and maintaining a strong security posture. Perform vulnerability scans, penetration tests, and security audits to identify and remediate any weaknesses in your cloud infrastructure.
- Cloud Provider Selection and Due Diligence: Choosing a reputable and reliable cloud service provider is vital to ensuring the security of your cloud environment. Conduct thorough due diligence when selecting a CSP, evaluating their security practices, compliance certifications, and data protection mechanisms.
Ensuring robust cloud security is of paramount importance for the sustainability of businesses. The cloud provides tremendous benefits, but it also introduces unique security challenges. By implementing a comprehensive security strategy encompassing encryption, strong access controls, monitoring mechanisms, regular updates, and employee education, businesses can bolster their cloud security posture and avoid financial losses due to security breaches.
Cloud security is a shared responsibility between the cloud hyperscaler and the customer. It is crucial to understand the division of responsibilities to ensure comprehensive security. While the CSP is responsible for securing the underlying cloud infrastructure, the customer must secure their applications, data, and access to the cloud services.
How Can Hexaware Help?
As part of our cloud transformation strategy design for customers, we build robust and purpose-built cloud foundations that align with customers’ business priorities, technical requirements, security, and compliance requirements. Our years of experience in Cloud Transformation services enable us to develop security best practices, design principles, and frameworks to ensure robust cloud security. Our breadth of solution offerings includes the following:
- Deployment of robust cloud security foundation through landing zones.
- Security Risk assessment and mitigation recommendations.
- Implementation of tools and frameworks for Cloud Security Management
- Assessment and enablement of frameworks and specific compliance and regulations such as CIS, NIST, PCI, HIPPA, SOX, GDPR, etc.
Our Amaze® platform, plays a significant role in helping enterprises mitigate their cloud migration risks and challenges, thereby providing a robust, industry-best solution.
For more information on our services and capabilities, please write to us at marketing@hexaware.com or visit https://hexaware.com.
About the Author

Maneesh Kale
Read more
Related Blogs

Understanding Snowflake Cortex for Gen AI Applications with Sensitive Data
- Generative AI
- Cloud
- Data & Analytics

Ready to Pursue Opportunity?
Every outcome starts with a conversation