This website uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies
The Heart and Soul of HDFS
Data & Analytics
November 1, 2013
Hadoopdistributed file system (HDFS) which is specifically designed for very large file storing with very large streaming access patterns running on clusters of commodity hardware. Hadoop is fault tolerant, scalable and extremely simple to expand.It has three main daemons namely
- NameNode
- DataNode
- Secondary NameNode
In this blog, we would be reading about these daemons and read/write operation using rack topology.
Namenode:
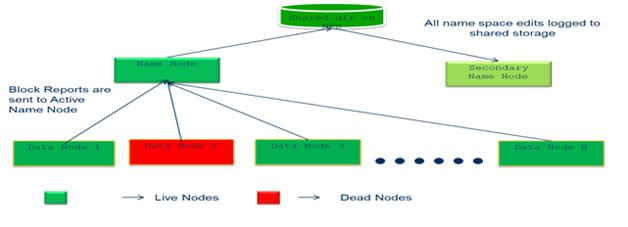
NameNode demon runs on a master server that manages the metadata information of the hadoop. When a NameNode starts up, it reads HDFS state from an image, fsimage, and then applies edits from the edits log file. It then writes new HDFS state to the fsimage and starts normal operation with an empty edits file. Both fsimage and edits log files present in the native file system of the hadoop. Clients contact NameNode for file metadata or file modifications and perform actual file I/O directly with the DataNodes. The NameNode executes file system namespace operations like opening, closing and renaming files and directories. It also determines the mapping of blocks to DataNodes.
DataNode:
DataNode demon runs on slave nodes and stores the actually data inside the HDFS, there are a number of Datanodes, usually one per node in the cluster, which manage storage attached to the nodes that they run on. HDFS exposes a file system namespace and allows user data to be stored in files. Internally, a file is split into one or more blocks and these blocks are stored in a set of Data Nodes. The DataNodes perform block creation, deletion, and replication of data as per the NameNode’s Instruction. The active datanodes are live nodes and the inactive datenodes are dead nodes.
Secondary NameNode:
The secondary NameNode demon is to take a snapshot of Name node which merges the fsimage and the edits log files periodically and keeps edits log size within a limit. It is usually run on a different machine than the primary NameNode since its memory requirements are on the same order as the primary NameNode. The secondary NameNode stores the latest checkpoint in a directory which is structured the same way as the primary NameNode’s directory So that the check pointed image is always ready to be read by the primary NameNode if necessary.
Fig. 1 – HDFS Architecture
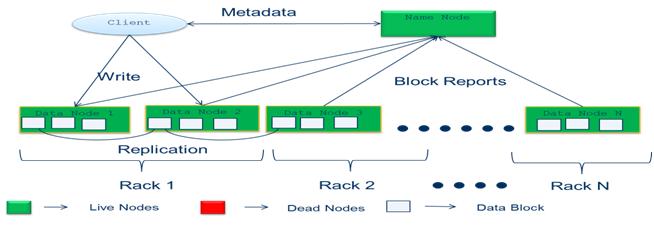
Write Operation:
- Client connects to the NameNode
- NameNode places an entry for the file in its metadata, returns the block name and list of Data Nodes to the client
- Client connects to the first DataNode and starts sending data
- As data is received by the first DataNode, it connects to the second and starts sending data
- Second DataNode similarly connects to the third and ack packets from the pipeline are sent back to the client
- Client reports to the NameNode when the block is written
- As the blocks are written, a checksum is also calculated and written to ensure the integrity of the data
Fig. 2 Write Operation
Replication strategy:
- First copy of the block is placed on the same node as the client
- If the client is not part of the cluster, the first block is placed on a random node
- System tries to find one which is not too busy
- Second copy of the block is placed on a node residing on a different rack
- Third copy of the block is placed on different node in the same rack as the second copy
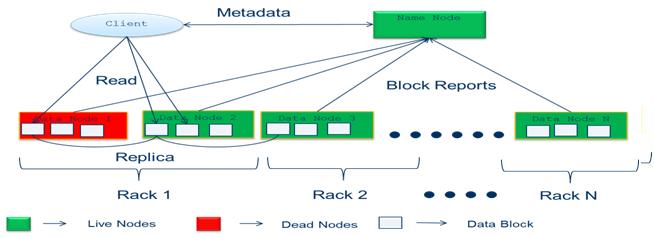
Read Operation:
- Client connects to the NameNode
- NameNode returns the name and locations of the first nearest blocks of the file
- Client connects to the first of the DataNodes, and reads the block
- If the DataNode fails during the read, the client will seamlessly connect to the next one in the list to read the block
Fig. 3 Read Operation
Related Blogs

Enterprise Data Services: The Backbone of Modern Businesses
- Data & Analytics

Navigating Databricks’ Delta Lake Features and Type Widening
- Data & Analytics

Top 13 Data Science Services Providers: Bridging the Gap Between Data Capabilities and AI Strategy
- Data & Analytics

The Role of AI in Automating SAS to PySpark Conversion and Accelerating Data Migration
- Data & Analytics

How to Achieve New Standards in Data Quality and Observability using Databricks Lakehouse Monitoring
- Data & Analytics

Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) on Amazon Bedrock
- Data & Analytics

Databricks Unity Catalog for Comprehensive Data Governance
- Data & Analytics

Ready to Pursue Opportunity?
Every outcome starts with a conversation