It is a given that today’s enterprises need to be flexible and adaptable to the changing market conditions and customer preferences. As a result, corporate executives often form great strategies and drive sweeping initiatives like digital transformation programs. But when the execution happens, the actual benefits are very often only partially realized, if at all.
Some of the reasons for this gap between strategy and execution are:
- Lack of analysis and refinement of strategy to ensure it is achievable, considering the realities of capital, products, markets and people
- Differences in opinion on the strategy across various levels of the organization
- Low correlation or connection between financial and operational models and results
- Low agreement on what the right measures should be to see how well the strategic objectives are being realized
- Uncertainty about the accuracy of the numbers seen in reports
- Low understanding of root causes as to why the company underachieves or achieves results
EPM (Enterprise Performance Management) was designed to bridge the gap between strategy and execution. It’s a management approach that involves and defines everyone’s roles in strategy, that gives them the tools and processes to execute based on focus, alignment, and accountability. It monitors performance across the enterprise by integrating and analyzing data from multiple sources. The promise of EPM is to provide a closed-loop framework for decision making, resource deployment, fewer surprises, and new insights.
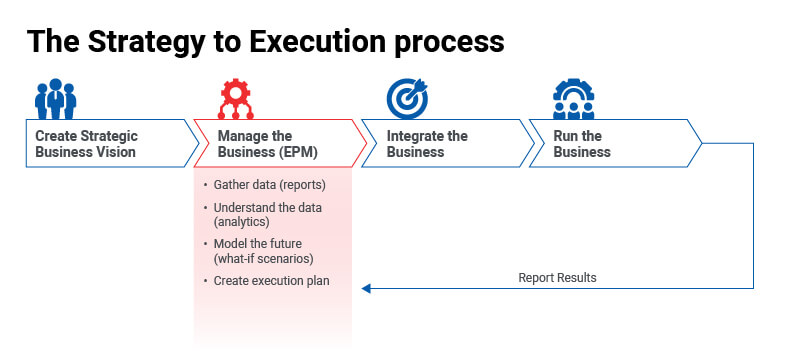
Enterprise Performance Management is basically about doing 3 things right:
- A framework that can be used to direct, guide, prioritize, organize, and optimize your resources
- The right technologies that are put in place to deliver on the framework’s processes
- A roadmap to realize your strategic vision based on the data fed into the framework
Benefits of EPM
1. Better Management Efficiency
EPM leverages investments made in ERP, CRM, Supply Chain Management, Salesforce automation and other transactional systems to perform standard management processes more efficiently:
- Budgeting, planning and forecasting
- Financial consolidation and statutory reporting
- Management reporting and business intelligence
- Profitability analysis
- Other financial and operational modeling, planning, analysis, and reporting
Some of the common types of EPM plans created as part of management processes:
- Strategic Plans: Annual Budget, Cashflow forecast, Balance Sheet plan
- Financial Plans: Revenue and Expense Plan, Sales plan, CAPEX plan
- Operational Plans: Workforce plan, Project financial plan, Marketing, Demand
- Forecasts: Sales forecast, Expense forecast, Demand forecast, Project forecast
These plans are stored separately in a combined multidimensional OLAP and relational store. This helps in analysis and business intelligence.
Best practices in the planning process:
- The real value drivers of the business should be explored and the right scenario for success, including validated targets, should be used to create the plans.
- The planning processes uncover new constraints that should be used to improve the financial and operational models.
- Financial and Operational Plans should be correlated, covering all areas of the business and shared across to help make optimal decisions.
- Forecasts and plans should be quickly adjusted based on actual results and variances from expected results. This gives the organization its competitive advantage.
- The budgeting, planning and forecasting processes should be correlated back to the financial and operational models that link strategy to plans.
2. Better Execution of Strategy
EPM can help you understand the relationship between what you want to happen in the business (and how) and what is likely to happen or actually happened (and why) by:
- Creating business models to achieve strategic business targets and documenting assumptions, constraints, and drivers
- Connecting those models to your annual operating plans, budgets, and forecasts
- Monitoring and alerting exceptional variances from actual to plan
- Helping identify the root causes of variance and feeding back that knowledge into the business model and strategy
- Tying it all together with a common business language and common master data to improve visibility, focus, and alignment, enabling more stakeholder alignment
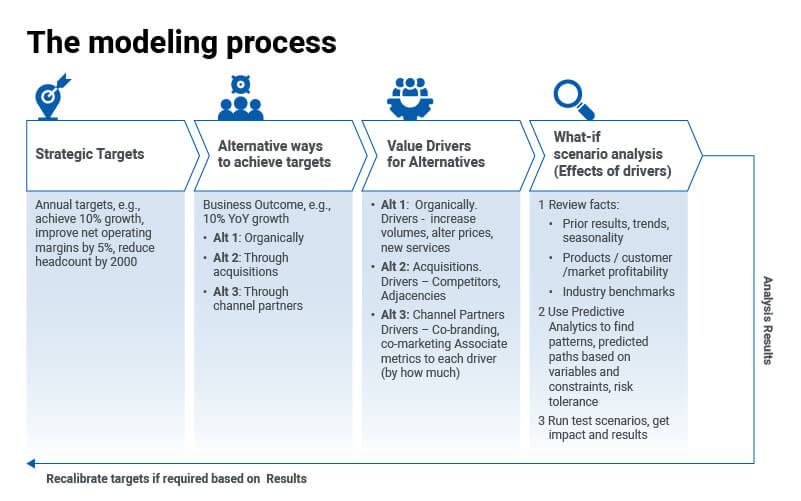
A common business language can be created through
- Common data and metadata: Same data is used to analyze root causes and see trends
- Common definitions, algorithms, and formulae: Cost allocation methods
- Common hierarchies: Common data roll-ups, e.g., by BU, Geo, product line, cost center
- Common business rules: How sales volume changes with price levels
- Common security: User roles and access, policies
3. Better business performance
EPM can impact the top and bottom line, the balance sheet, and the overall return on capital by enabling better business decisions based on timely, relevant information. Here are some benefits:
- Improved visibility into the key drivers of value in the business
- Visibility into the cause-and-effect relationship of operational metrics on financial performance
- Helps focus on the right things in the business
- Brings agility to business models and organizational structures
The key is to use information for better fact-based decisions, resource utilization and accountability. Some of the qualities of information that increase its impact are:
- Relevance – Does the information have material impact on the business, e.g., sales, gross margin, product quality or customer satisfaction
- Volatility – If data changes frequently, e.g., commodity prices, increasing its urgency
- Variance – How much did the data vary to what you planned for, and what is your tolerance for that variation?
- Cross impact – Does the data affect other areas of business, e.g., travel expense affects selling, general, and administrative (SG&A) expense and operating margin
- Reach – Provide the correct level of data to the correct people in the organization
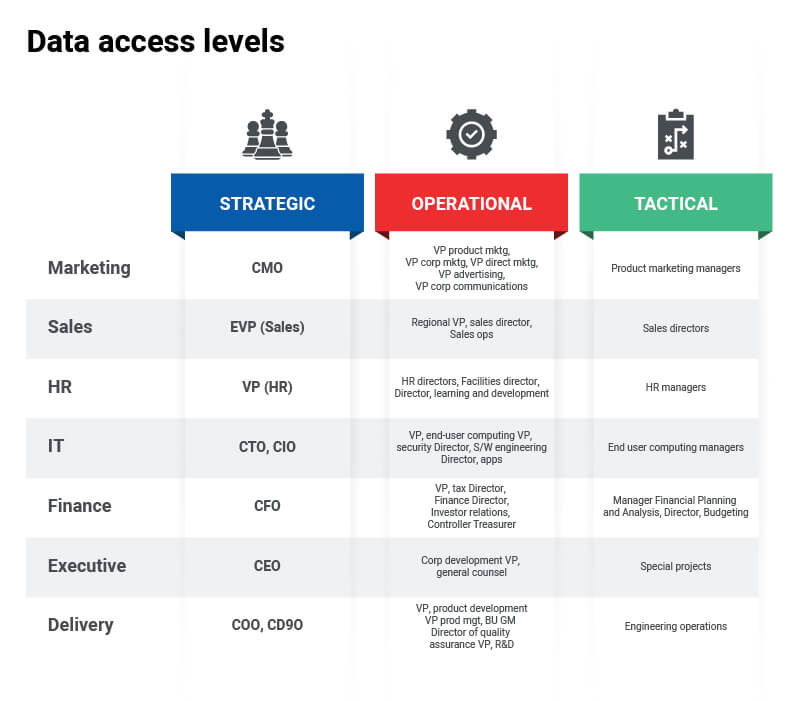
Table: An example of a matrix where data is mapped to the right set of people in an organization
4. Reduced Risk
By improving transparency and providing access of the right information to the right consumers, employees can see for themselves where the business is, and managers can test operational and financial models to help make the best resource deployment decisions:
- Global governance and compliance of data and reporting
- Accountability for results
- Better preparation for change, increased predictability
- Fewer surprises through better collaboration and communication
Standardized reporting enables compliance with statutory bodies like GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Procedures) or IRFS (International Financial Reporting Standards).
Enterprise Accountability is the idea of making sure all levels and all functions of the business are working on their part of executing the corporate strategy. IT systems should be tailored for the appropriate intersection of layer and function in an organization and should come with visibility and insight into each employee’s contribution. This visibility, combined with a public measurement system, reduces the risk of not achieving targets.
5. More Competitive Advantage
Organizations that get EPM right through the following are more agile than those who don’t:
- Better strategy formulation and planning
- Less complexity and lower costs by unifying management information
- Increased organizational flexibility (mergers and acquisitions, organizational changes)
Information based on reality, showing where the numbers come from and being able to drill down into the details, and what people are working on is connected to overall company objectives helps make faster decisions with confidence.
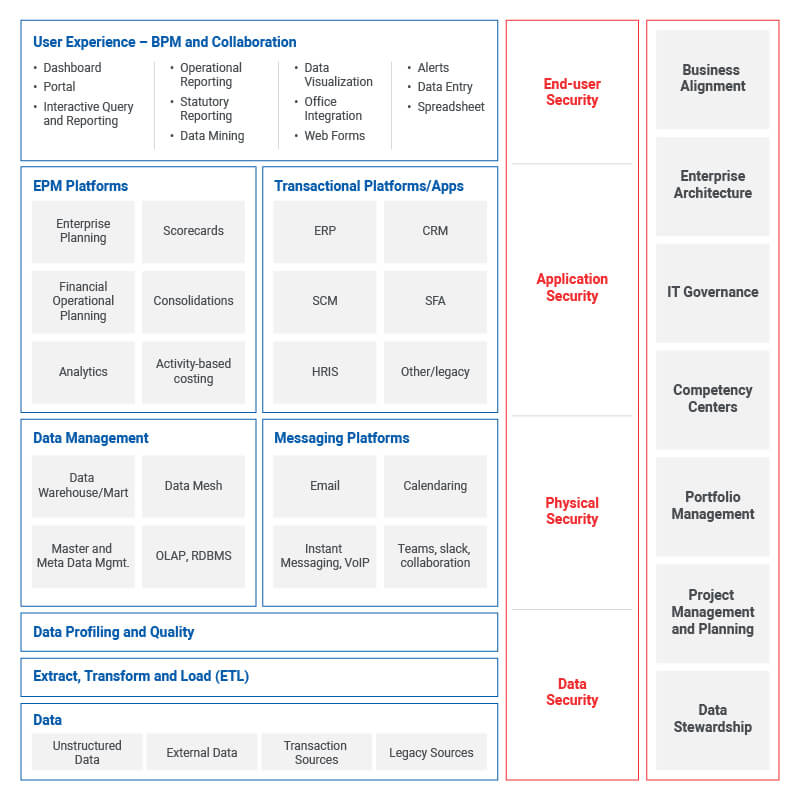
4 areas: the people, the process, the technology, and the data, should work in concert to drive toward a common goal: developing the most realistic, probable model that helps optimize resources and deliver on strategic goals.
Strategic flexibility – You should have a variety of models for different economic and competitive scenarios ready at hand, especially when market conditions change. How fast and how accurately you respond to market events determines your competitive advantage.
Conclusion
EPM demands alignment. You can have the most advanced technical infrastructure, the latest business process management (BPM) tools, high-quality data, executive sponsorship, and well-defined EPM processes, but unless these are financially and operationally aligned—across functions and through all layers of the business—with your organizational ecosystem and your overarching strategy, you won’t achieve the best return on your EPM investment.
References:



















