Distributed Agile Delivery Model is an Agile Global delivery framework focusing on multi-shore project delivery enabling both dispersed and distributed teams to have successful business value delivery.
The Agile Edge:
In the software industry, Global Software Development (GSD) has become a common practice and has its own advantages for eg; solving local IT skill shortage while offering cost efficiencies. However, GSD becomes challenging because teams have to deal with time-based, topographical and socio-cultural distance, resulting in difficulties with division of work, scarce communication, knowledge management, project and process management issues and infrastructure problems.
Agile Software development has grown significantly over the past decade, according to the 10th Annual State of Agile Survey . There is an incremental rise in the number of large enterprises that are embracing agile every year. The survey states that more than 82% of respondents had some distributed teams practicing agile at some level within their organization. This figure has seen a steep rise from 35% recorded in 2012.
A co-located agile team has an open flow of information exchange amongst all its team members. General awareness, communication and information radiators in a co-located set-up back agile principles. Ownership reins in collective responsibility, less documentation and simple design, leading to effective collaboration. Information sharing has to be fully and clearly expressed in a distributed agile team where team members are spread across various locations.
Understanding enablers for distributed Agile can quicken business delivery for establishments. Effective collaboration, increased team productivity and project visibility are some of the benefits businesses can gain if certain alignments are made in the current working model.
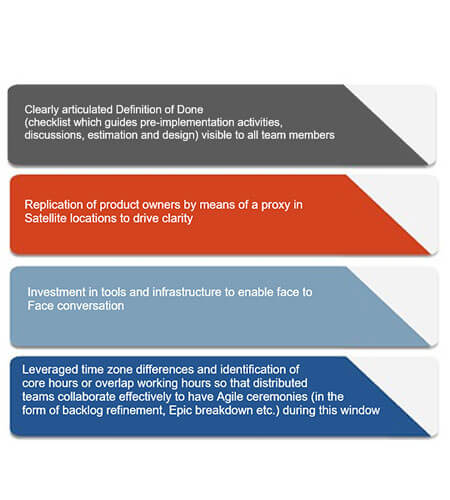
Distributed Agile Best Practices:
These best practices need to be followed in a distributed agile team to minimize ambiguity.
Governance: Backbone of Successful Distributed Teams:
Imagine a situation where projects are spread across various geographies and time zones with employees coming in from multiple points like project sponsor organization, vendors and independent contractors. This increases complexity, thereby making it essential to form a governance team that comprises of representatives from all locations and work in unison to run distributed projects successfully.
A few points to keep in mind:
- Establishing a shared vision on the current project or group of projects across governance team members is important. Every Project will have well-defined goals and milestones and clearly-identified consistent success parameters at governance level. Without this step, the governance team will tend to focus on transactional issues and might miss the big picture. Success parameters should be identified beyond tested code and low value documentation
- Periodic steering committee reviews are imperative to comprehend and develop performance of distributed Agile Projects. It’s important to identify specific measurable action items that are truthful and time bound at the end of each review and systematically track them to closure, thereby ensuring positive reinforcement in governance
Distributed Agile will be increasingly adopted by clients for reasons like business continuity and cost effectiveness over the coming years. Distributed Agile delivery process along with implementation of XP techniques will help teams to improve code quality and minimize technical debts leading to delivery of scalable software.
References
1. 10th Annual State of Agile Survey



















