The Rising Demand for ESG Initiatives
As concerns over our planet’s environmental health have increased, governing bodies around the world have set various targets for manufacturing companies to meet. These targets push companies to track their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) measures and continuously report said numbers to key stakeholders through various ESG Frameworks. For example, the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) provides guidelines on climate-related financial risks. The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) offers standards for sustainability accounting. The Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) mandates energy and carbon reporting. The Natural Gas Global Reporting (NGGR) focuses on reporting within the natural gas sector, and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG) guide companies towards broader global sustainability targets.
As manufacturing companies strive to meet these stringent ESG targets, they find that robust ESG practices not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also enhance their overall sustainability and operational efficiency. This alignment with ESG standards helps companies mitigate risks, improve resource management, and foster innovation, ultimately contributing to their long-term viability and success. Consequently, businesses that excel in ESG compliance are becoming more attractive to investors who are increasingly prioritizing sustainability in their investment strategies.
Global sustainable investment is now at $30.3 Trillion, up 68% since 2014. The increase is due to the focus of stakeholders and investors on ESG compliances and companies’ realization of the long-term success ESG compliance can bring in terms of cost and operations optimizations. The Assets Under Management (AuM) related to ESG is expected to rise by 12% to 33.9 trillion by 2026 (PwC), underscoring the growing significance of ESG assets for the manufacturing industry.
Current Landscape: ESG Reporting Challenges
As the manufacturing industry moves towards ESG compliance, it faces inherent challenges. Organizations must navigate various frameworks to report data on different ESG factors such as climate, greenhouse gas emissions, decarbonization, environmental, health and safety concerns, and more.
One significant hurdle is the need to tailor reports to different stakeholders’ requirements. Each stakeholder group, whether investors, regulators, customers, or employees, may demand specific sets of ESG data and metrics. Consequently, companies often find themselves drafting multiple reports, each tailored to meet the needs of a particular audience. This process can be time-consuming, resource-intensive, and prone to inconsistencies, leading to inefficiencies in reporting practices.
Furthermore, while ESG standards typically mandate annual reporting to external stakeholders, internal stakeholders require more frequent updates and insights. Regular communication with internal teams is crucial for reinforcing baseline ESG conditions, identifying emerging risks, and implementing timely mitigation strategies. This ongoing dialogue is essential for driving continuous improvement in ESG performance and ensuring alignment with broader sustainability goals, such as achieving net-zero emissions targets.
In addition to these operational challenges, manufacturing organizations must grapple with evolving regulatory landscapes and reporting frameworks. Keeping pace with changing regulations, emerging standards, and stakeholder expectations requires ongoing monitoring, adaptation, and investment in ESG reporting capabilities.
Addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach, using emerging disruptive technologies to prioritize transparency, collaboration, and innovation in ESG reporting practices. That’s where generative AI can be a game changer for the manufacturing industry.
The Advent of AI: ESG Reporting Made Effortless
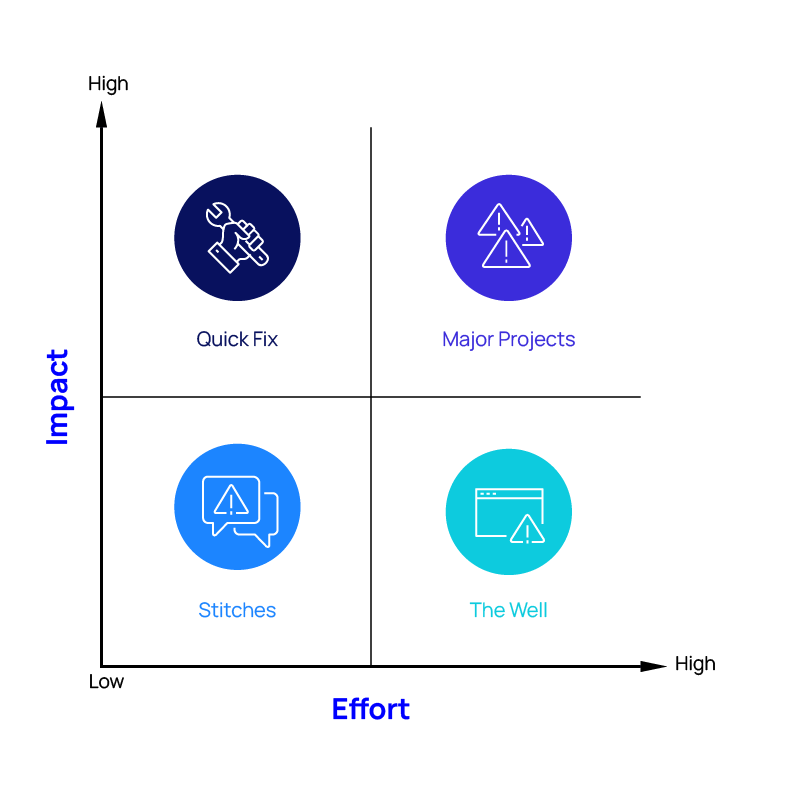
With the introduction of generative AI, we can automate the task of ESG reporting. Gen AI can provide various information about ESG, based on business operation data (emissions, water usage, circular economy) and risks assessed by double materiality: financial materiality and materiality to market, environment, and people. By combining Gen AI and IoT infrastructure, a company can automatically share ESG data with the internal stakeholders, who can use it to make better decisions. For example, AI modelling can be used to rank the effect and probability of each ESG task leveraging a simple but useful tool known as the Impact Effort Matrix or Eisenhower Matrix. Tasks are classified into four quadrants: important and high effort (Major Projects), important and low effort (Quick Fix), urgent but not important (The Well), and neither urgent nor important (Stitches). This classification helps individuals or teams concentrate on what is most important and use their time effectively.
Once the risks have been studied, they are prioritized into the buckets given above. Usually, programs containing Quick Fixes and Major Projects are carried out. The inclusion of Stitches depends upon the stakeholders and business goals. Tasks falling into the Well are generally not addressed, as it is a lot of work to solve a minuscule event. Therefore, a mitigation strategy is developed to address the risk.
Risk prioritization and data from IoT infrastructure help companies develop an As-Is and To-Be scope for projects by aligning the available data to business goals and timelines.
ESG data is gathered from IoT infrastructure and applications to monitor operational performance and is routed through connectors to consolidate in a central data warehouse. Subsequently, this data undergoes cleaning and categorization into operational categories such as emission, water treatment, electricity usage, EHS (Environment, Health & Safety), decarbonization levels, and climate data. Within these categories, factors like greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1, 2, and 3), water toxicity level, employee injuries, and carbon footprint are analyzed to extract insights and inform decision-making to mitigate risks regularly.
Utilizing AI, insights are generated through the Impact Effort Matrix, facilitating the formulation of mitigation strategies. Gen AI carries out reports per established reporting frameworks for internal and external stakeholders.
Challenges to Using Gen AI for ESG Reporting
However, the process has challenges that must be addressed in the planning phase to avoid disruptions or downtime between programs.
- Data Quality and Availability: Generative AI relies heavily on high-quality and reliable data for training models and generating reports. However, ESG data can be fragmented, inconsistent, and of varying quality, making it challenging to ensure the accuracy and reliability of AI-generated reports.
- Regulatory Compliance: ESG reporting is subject to various regulatory frameworks, standards, and guidelines, which may evolve over time and vary across jurisdictions. Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements while leveraging generative AI can be challenging, requiring ongoing monitoring and adaptation of reporting practices.
- Human Oversight and Expertise: While generative AI can automate many aspects of ESG reporting, human oversight and expertise are still necessary to validate outputs, interpret results, and make informed decisions. Integrating human judgment with AI capabilities is essential for ensuring the accuracy, relevance, and ethical use of AI-generated reports.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: Generative AI relies on large datasets, raising concerns about cybersecurity risks and data privacy issues. Protecting sensitive ESG data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse is critical for maintaining trust and integrity in ESG reporting practices.
Benefits of Using Gen AI for ESG Reporting
Once the challenges discussed above are addressed, companies can leverage generative AI in ESG reporting, which provides a wide range of benefits:
- Process Optimization: Generative AI can automate the generation of ESG reports, saving time and resources for organizations by automating repetitive tasks such as data collection, analysis, and report generation.
- Data management: Generative AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data from various sources and formats, which enables organizations to analyze complex ESG-related information more effectively, identify trends, and extract valuable insights to inform decision-making.
- Performance Standardization: Generative AI can help improve the accuracy and consistency of ESG reporting by minimizing human error and bias and enhancing the reliability and credibility of ESG disclosures.
- Scenario Modeling and Predictive Analytics: Generative AI can facilitate scenario modeling and predictive analytics. By simulating various scenarios and predicting outcomes, organizations can make more informed decisions to optimize their ESG performance and mitigate risks.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Transparency: Generative AI-powered ESG reporting can enhance stakeholder engagement and transparency by providing timely and relevant information about the organization’s ESG performance.
- Innovation and Continuous Improvement: Generative AI can support innovation and continuous improvement in ESG reporting by enabling organizations to explore new data sources, metrics, and analytical techniques.
- Customization and Personalization: Generative AI can generate customized ESG reports tailored to the specific frameworks and preferences of different stakeholders.
Generative AI can report ESG parameters along all the scopes of GHG emissions and with any factor that sensors can measure. Internal stakeholders can leverage the data from sensors to improve efficiency and optimize operations. It can also generate reports based on customized frameworks according to the preferences of the stakeholders. It can be a game changer for the manufacturing industry in tracking ESG factors and continuously improving to move on towards net zero goals as it brings a level of visibility inside the organizations needed to optimize every business function.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future Through Generative AI
The integration of generative AI in ESG reporting marks a significant advancement for the manufacturing industry. By automating and optimizing the complex process of ESG data collection, analysis, and reporting, companies can meet stringent regulatory requirements and enhance their sustainability practices. This not only supports operational efficiency and risk mitigation but also aligns with the growing trend of sustainable investing.
Investors are increasingly prioritizing companies with strong ESG performance, recognizing that these companies are better positioned for long-term success. The ability to provide transparent, accurate, and timely ESG reports makes manufacturing companies more attractive to these investors, thereby driving more capital into sustainable ventures. As a result, the adoption of generative AI for ESG reporting not only facilitates compliance and operational improvements but also opens up new opportunities for investment and growth.
In an era where sustainable investment is rapidly growing, manufacturing companies that leverage generative AI for ESG reporting can achieve a competitive edge. They can attract a broader base of investors who are focused on sustainability and are likely to benefit from increased financial stability and market resilience. By integrating AI-driven ESG reporting into their business strategies, manufacturing firms can pave the way for a more sustainable and prosperous future.
How Hexaware can Help
From ESG reporting automation to innovative solutions for operational efficiency and regulatory compliance, Hexaware empowers you to achieve your sustainability goals and attract more investors. Ready to make a difference? Explore Hexaware’s Sustainability Services today and lead the way to a greener future.